How Did Lake Superior Get Its Name
| Lake Superior | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Coordinates | |
| Main sources | Nipigon River, St. Louis River Dove River Pic River White River Michipicoten River Kaministiquia River |
| Main outflows | St. Marys River |
| Basin countries | Canada, Us |
| Max length | 563 km (350 mi) |
| Max width | 257 km (160 mi) |
| Surface area | 82,414 km² (31,820 mi²)[1] Canadian portion 28,700 km² (11,080 mi²) |
| Average depth | 147 yard (482 ft) |
| Max depth | 406 thousand (1333 ft)[1] |
| Water volume | 12,100 km³ (2900 mi³) |
| Residence fourth dimension (of lake water) | 191 years |
| Shore lengthone | 4385 km (2725 mi) |
| Surface tiptop | 183 m (600 ft)[1] |
| Islands | Isle Royale Apostle Islands |
| Settlements | Duluth, Minnesota Superior, Wisconsin Thunder Bay, Ontario Marquette, Michigan Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario |
| 1 Shore length is an imprecise measure which may non be standardized for this commodity. | |
Lake Superior, divisional by Ontario, Canada, and the U.S. country of Minnesota to the northward, and u.s.a. of Wisconsin and Michigan to the south, is the largest of North America's Slap-up Lakes. Receiving water from approximately 200 rivers, it is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface area and is the world'due south third-largest freshwater lake by volume. Its shoreline is almost 2,800 miles long.
Contents
- one Proper noun
- two History
- three Geology
- 4 Geography
- iv.1 Hydrography
- 4.2 Tributaries and outlet
- 4.3 Climate
- v Ecology
- 6 Aircraft
- vi.one Shipwrecks
- 7 Notes
- 8 References
- nine External links
- x Credits
With an average depth budgeted 500 feet, it is also is the coldest and deepest (1,332 feet at its deepest point) of the Swell Lakes. Its drainage basin covers 49,300 square miles. Most of the bowl is sparsely populated, and heavily forested, with fiddling agronomics because of a cool climate and poor soils.
Proper noun
In the Ojibwe linguistic communication, the lake is called "Gichigami" (Shining Large-Sea-H2o), only it is improve known equally "Gitche Gumee," as recorded by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow in "The Song of Hiawatha." Lake Superior is referred to as "Gitche Gumee" in the song "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald," by Gordon Lightfoot.
The lake was named le lac supérieur, or "Upper Lake," in the seventeenth century by French explorers because it was located in a higher place Lake Huron.
History
The first people came to the Lake Superior region 10,000 years agone later the retreat of the glaciers in the final Ice Age. They were known equally the Plano, and they used stone-tipped spears to hunt caribou on the northwestern side of Lake Minong.
The next documented people were known as the Shield Archaic (c. 5000-500 B.C.E.). Evidence of this culture tin exist establish at the eastern and western ends of the Canadian shore. They used bows and arrows and dugout canoes; fished, hunted, mined copper for tools and weapons, and established trading networks. They are believed to be the direct ancestors of the Ojibwe and Cree.[2]
The Laurel people (c. 500 B.C.E. to 500 C.Eastward.) adult seine cyberspace angling, co-ordinate to prove in rivers elimination into Superior such as the Pic and Michipicoten.
Some other culture, known as the Concluding Woodland Indians (c. 900-1650 C.E.), has been found. They were Algonquan people who hunted, fished, and gathered berries. They used snowfall shoes, birch bark canoes, and conical or domed lodges. Nine layers of their encampments have been discovered at the oral fissure of the Michipicoten River. Most of the Pukaskwa Pits were likely made during this time.[ii]
The Anishinabe, also known as the Ojibwe or Chippewa, have inhabited the Lake Superior region for over v hundred years, and were preceded past the Dakota, Fox, Menominee, Nipigon, Noquet, and Gros Ventres. They chosen Lake Superior Anishnaabe Chi Gaming, or "the Ojibwe's Ocean." Later the arrival of Europeans, the Anishinabe fabricated themselves the eye-men between the French fur traders and other Native peoples. They soon became the dominant Indian nation in the region: they forced out the Sioux and Fox and defeated the Iroquois west of Sault Ste. Marie in 1662. By the mid-1700s, the Ojibwe occupied all of Lake Superior'southward shores.[2]
In the 1700s, the fur trade in the region was booming, with the Hudson'southward Bay Visitor (HBC) having a virtual monopoly. In 1783, however, the N Due west Company (NWC) was formed to compete with HBC. The NWC built forts on Lake Superior at K Portage, Nipigon, the Movie River, the Michipicoten River, and Sault Ste. Marie. But past 1821, with competition taking too smashing a cost on both, the companies merged under the Hudson's Bay Company name.
Many towns around the lake are either electric current or sometime mining areas, or engaged in processing or aircraft. Today, tourism is another significant industry as the sparsely populated Lake Superior state, with its rugged shorelines and wilderness, attracts tourists and adventurers.
Geology
Lake Superior's North Shore dates back to the ancestry of the earth. Virtually 2.7 billion years ago, magma forcing its way to the surface created the intrusive granite rock of the Canadian Shield. This rock sank into the mantle numerous times, finally rising and cooling to become the formations that tin can exist seen on the N Shore today. It was in this period, the Kenora Orogeny, that many valuable metals were deposited. This is why the country surrounding the lake has proved to be rich in minerals. Copper, iron, silvery, gold, and nickel are or were the most often mined. Examples include the Hemlo gold mine near Marathon, copper at Point Mamainse, silver at Silver Islet, and uranium at Theano Point.

Pictographs at Lake Superior Provincial Park, Ontario.
The mountains steadily eroded starting about 2.49 billion years ago, depositing layers of sediment which compacted and became limestone, dolostone, taconite, and the shale at Kakabeka Falls.
Virtually i.i billion years agone, the continent drifted autonomously, creating one of the deepest rifts in the world. The lake lies above this long-extinct Mesoproterozoic rift valley, the Midcontinent Rift, which explains its great depths. Magma was injected between layers of sedimentary rock, forming diabase sills, a hard rock which resists corrosion. This difficult diabase protects the layers of sedimentary rock beneath, forming the flat-topped mesas in the Thunder Bay surface area.
Lava erupting from the rift cooled, forming the black basalt stone of Michipicoten Island, Black Bay Peninsula, and St. Ignace Island.
Effectually ane.vi million years ago, during the last Great Ice Historic period, ice covered the region at a thickness of i.25 miles (2 km). The land contours familiar today were carved by the accelerate and retreat of the ice sail. The retreat, x,000 years ago, left gravel, sand, dirt, and boulder deposits. Glacial meltwaters gathered in the Superior bowl creating Lake Minong, a precursor to Lake Superior.[2] Without the immense weight of the ice, the country rebounded, and a drainage outlet formed at Sault Ste. Marie, which would go known as St. Mary'south River.
Geography
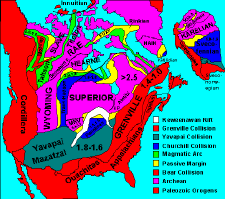
North American cratons and basement rock, showing the formation of the Midcontinent Rift containing today's Lake Superior.
The largest island in Lake Superior is Isle Royale, function of the U.Southward. country of Michigan, off the Upper Peninsula. Other big islands include Madeline Island in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and Michipicoten in the Canadian province of Ontario.
The larger towns on Lake Superior include: The twin ports of Duluth, Minnesota and Superior, Wisconsin; Thunder Bay, Ontario; Marquette, Michigan; and the 2 cities of Sault Ste. Marie, in Michigan and in Ontario. Duluth, at the western tip of Lake Superior, is the most inland bespeak on the Saint Lawrence Seaway and the near inland port in the globe.
Among the scenic areas on the lake are: The Apostle Islands National Lakeshore; Isle Royale National Park; Pukaskwa National Park; Lake Superior Provincial Park; Yard Island National Recreation Area; Sleeping Behemothic (Ontario); and Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore.
Hydrography
Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface expanse. Lake Baikal in Russian federation is larger by book, as is Lake Tanganyika. The Caspian Sea, while vastly larger than Lake Superior in both area and volume, is saline; presently isolated, in the past, it has been repeatedly continued to, and isolated from, the Mediterranean via the Black Sea.
Did you know?
Lake Superior, the largest of the North American Great Lakes, is the largest freshwater lake in the globe by surface expanse
Lake Superior (48°00'N, 88°00'W) has a surface area of 31,820 foursquare miles (82,414 km²)[one]—which is larger than the U.S. state of South Carolina. Information technology has a maximum length of 350 miles (563 km) and maximum width of 160 miles (257 km). Its average depth is 483 feet (147 1000) with a maximum depth of 1,333 feet (406 thou).[i] Lake Superior contains 2,900 cu mi (12,100 km³) of water. There is enough water in Lake Superior to embrace the unabridged land mass of North and Southward America with a foot (30 cm) of h2o. The shoreline of the lake stretches two,726 miles (4,385 km) (including islands). The lake's peak is 600 feet (183 1000)[ane] above bounding main level. American limnologist J. Val Klump was the first person to reach the lowest depth of Lake Superior on July 30, 1985, as part of a scientific expedition.
Almanac storms on Lake Superior regularly record wave heights of over twenty feet (six m). Waves well over thirty feet (9 m) have been recorded.[2]
Water levels, including diversions of water from the Hudson Bay watershed, are governed past the International Lake Superior Board of Control which was established in 1914, by the International Joint Commission.
Tributaries and outlet
The lake is fed by over 200 rivers. The largest include the Nipigon River, the St. Louis River, the Pigeon River, the Moving picture River, the White River, the Michipicoten River, the Brule River, and the Kaministiquia River. Lake Superior drains into Lake Huron through the St. Marys River. The rapids on the river resulting from the 25 pes (7.six m) difference in elevation between Lake Superior and Lake Huron necessitated the building of the Sault Locks (pronounced "soo"), a part of the Great Lakes Waterway, to motion boats between the Lakes. The offset locks were built in 1855, between the twin cities of Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario and Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. In that location are now five locks; the largest of which is the Poe Lock.[3]
Climate

Lake Superior from Duluth, MN, Dec, 2004
Lake Superior's size creates a localized oceanic or maritime climate (more typically seen in locations like Nova Scotia). The water's tiresome reaction to changing temperatures helps to moderate surrounding air temperatures in the summertime and wintertime, and creates lake effect snow in colder months. The hills and mountains that border the lake form a basin, which holds wet and fog, specially in the autumn.
Ecology
Although part of a single system, each of the Great Lakes is different. In volume, Lake Superior is the largest. It is also the deepest and coldest of the five. Superior could contain all the other Not bad Lakes and three more than Lake Eries. Considering of its size, Superior has a retentivity time of 191 years, the longest recharge time of the five Lakes.
Co-ordinate to a study by professors at the Academy of Minnesota Duluth, Lake Superior has been warming faster than its surrounding climate. Summer surface temperatures in the lake take increased about four.5 degrees Fahrenheit since 1979, compared with about a ii.7-degree increment in the surrounding boilerplate air temperature. The increase in the lake'south surface temperature is not just due to climate change just likewise to the decreasing lack of ice cover. Less winter ice cover allows more solar radiation to penetrate the lake and warm the h2o.[4]
The Lake Superior Basin is dwelling house to many diverse micro-climates, environments, and habitats. Some of the more than unusual include the Kakagon Slough, sometimes referred to every bit the "Everglades of the North," a vast common cold h2o wetland encompassing 16,000 acres. Forth with other rare species, the Slough provides nesting areas for the threatened Piping plover, and nurseries for the ever shrinking population of lake sturgeon. Further north, the Algoma Highlands on the eastern shore of Lake Superior in Ontario is a rare example of old-growth forest. With near 30 inches (762 mm) of rainfall and 13 feet (4 meters) of snow annually, the forest is one of Canada'south most diversified biomes. The Lake Superior Highlands is some other setting for an immense range of plant and animal species living in rocky shoreline communities and old-growth hardwood forests. The undisturbed wild lands edging Lake Superior create habitats for blackness bears, lynxes, migrating raptors, including peregrine falcons and bald eagles. Considered "disjunct," these communities are threatened because the nearest neighboring habitats tin can exist hundreds of miles distant. Considerable effort is being expended to exit these habitats and environments intact despite encroaching development.
Shipping

The SS Edmund Fitzgerald, a typical lake freighter which sank in 1975
Lake Superior has been an of import link in the Great Lakes Waterway, providing a route for the transportation of iron ore and other mined and manufactured materials. Large cargo vessels called lake freighters, as well every bit smaller bounding main-going freighters, ship these commodities across Lake Superior. Cargo every bit varied equally taconite, coal, chromium ore, wheat, corn, beet lurid pellets, common salt, and wind turbine parts travel across Lake Superior in one calendar month.
Shipwrecks
The concluding major shipwreck on Lake Superior was that of SS Edmund Fitzgerald, in 1975.
Co-ordinate to an former sailor's tale, Lake Superior never gives upwardly her dead. This is due to the temperature of the h2o. Normally, leaner feeding off a sunken decaying body will generate gas within the torso, causing it to float to the surface after a few days. The h2o in Lake Superior however, is common cold enough year-round to inhibit bacterial growth, meaning bodies tend to sink and never surface.[2] This is poetically referenced in Gordon Lightfoot'southward famous ballad, "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald."
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.i 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 John W. Wright, (ed.), The New York Times Almanac (New York: Penguin Books, 2004, ISBN 0143038206).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 ii.iv 2.v Barbara Chisholm (ed.), Superior: Nether the Shadow of the Gods (Lynx Images, 1998, ISBN 978-0969842774).
- ↑ The Soo Locks Pure Michigan. Retrieved January 25, 2020.
- ↑ Study: Lake Superior is i of the fastest-warming lakes in the world MPR News, January xiv, 2016. Retrieved January 25, 2020.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Armbruster, Ann. Lake Superior. New York: Children's Printing, 1996. ISBN 0516200151.
- Beckett, Harry. Lake Superior. Vero Beach, FL: Rourke Corp., 1999. ISBN 0865935289.
- Chisholm, Barbara (ed.), Superior: Under the Shadow of the Gods. Lynx Images, 1998. ISBN 978-0969842774
- Prevost, John F. Lake Superior. Edina, MN: Abdo Pub., 2002. ISBN 1577651049.
- Wright, John West. (ed.). The New York Times Almanac. New York: Penguin Books, 2004. ISBN 0143038206
- Ylvisaker, Anne. Lake Superior. Mankato, MN: Capstone Printing, 2004. ISBN 0736822127.
External links
All links retrieved January 25, 2020.
- Lake Superior. The states Environmental Protection Bureau.
- Lake Superior Facts
- Lake Superior Magazine
- Lake Superior: Facts Near the Greatest Great Lake Live Science.
- Lake Superior Pure Michigan
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accord with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa three.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this commodity click here for a list of adequate citing formats.The history of earlier contributions past wikipedians is attainable to researchers here:
- Lake Superior history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
- History of "Lake Superior"
Note: Some restrictions may apply to apply of individual images which are separately licensed.
How Did Lake Superior Get Its Name,
Source: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Lake_Superior
Posted by: mattosminquirwas.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How Did Lake Superior Get Its Name"
Post a Comment